Future Market Analysis and Applications of High Temperature Heat Pumps
High temperature heat pumps (HTHPs) are rapidly emerging as a key technology in the global shift towards energy efficiency and decarbonization. With the ability to provide heat at temperatures up to 120–160°C or higher, HTHPs address a critical gap in industrial and commercial heating applications where traditional low-temperature heat pumps cannot perform.
Global Market Outlook
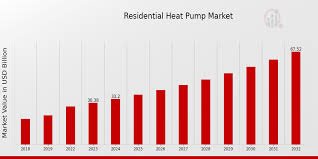
The global market for high temperature heat pumps is projected to grow significantly in the coming decade, driven by stringent climate policies, rising energy costs, and the need for sustainable industrial Solutions. According to industry reports:
• The global HTHP market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8–12% from 2025 to 2035.
• Europe and Asia-Pacific are leading markets, spurred by carbon neutrality targets and strong government incentives.
• Industrial applications account for over 60% of the demand, particularly in food processing, chemicals, paper, textiles, and district heating.
Key drivers include:
✅ Decarbonization Goals – Governments and industries aim to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by replacing fossil-fuel-based boilers.
✅ Energy Efficiency – HTHPs achieve Coefficients of Performance (COP) of 2.5–4.5, offering significant energy savings.
✅ Waste heat recovery – Utilizing industrial waste heat (40–90°C) to deliver process heat up to 160°C.
Main Application Areas
1. Food and Beverage Industry
• Used for pasteurization, drying, sterilization, and cleaning processes.
• Examples: Dairy processing, brewing, beverage production, and condiments manufacturing.
2. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries
• Provides process heat for reactors, distillation, and drying.
• Enables recovery of waste heat from condensation or cooling streams.
3. Textile and Paper Industries
• Supplies high-temperature air and water for drying, bleaching, and washing.
• Reduces reliance on steam boilers.
4. District Heating
• Supplies heat for centralized heating networks, replacing coal or gas-fired systems.
5. Metals and Plastics Processing
• Delivers heat for pre-heating, molding, and cleaning operations.
Future Trends and Innovations
• Higher Temperature Ranges: Development of next-generation HTHPs reaching 180–200°C for applications in chemicals and heavy industries.
• Natural Refrigerants: Adoption of environmentally friendly refrigerants such as CO₂ and ammonia for compliance with F-Gas regulations.
• Hybrid Systems: Integration with solar thermal and biomass systems for flexible and resilient energy supply.
• Smart Controls: AI and IoT-enabled systems for demand response and optimized operation.
Benefits for Industry
🌱 Reduced Carbon Emissions: Replace fossil-fuel boilers with renewable electricity-driven heat pumps.
💸 Lower Operating Costs: Cut energy bills by 30–50% with high COPs and waste heat recovery.
🏭 Process Optimization: Provide precise temperature control for sensitive industrial processes.
♻️ Sustainable Production: Support corporate ESG goals and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
High temperature heat pumps are set to play a pivotal role in the global energy transition. Their ability to deliver high-grade heat efficiently makes them an ideal solution for industries seeking to decarbonize and achieve long-term cost savings. As technology advances and policy support strengthens, HTHPs will become a cornerstone of sustainable industrial heating worldwide.