Definition
An electric heater alternative for industrial equipment refers to advanced heating Solutions that replace conventional resistive electric heaters with more energy-efficient, controllable, and reliable technologies.
Unlike traditional electric heaters that generate heat directly from electrical resistance, modern alternatives focus on moving and managing heat more intelligently, enabling consistent thermal performance under demanding industrial conditions.
In environments where process stability, continuous operation, and long service life are critical, these alternatives are increasingly regarded as strategic infrastructure upgrades.
Industry Pain Points Solved
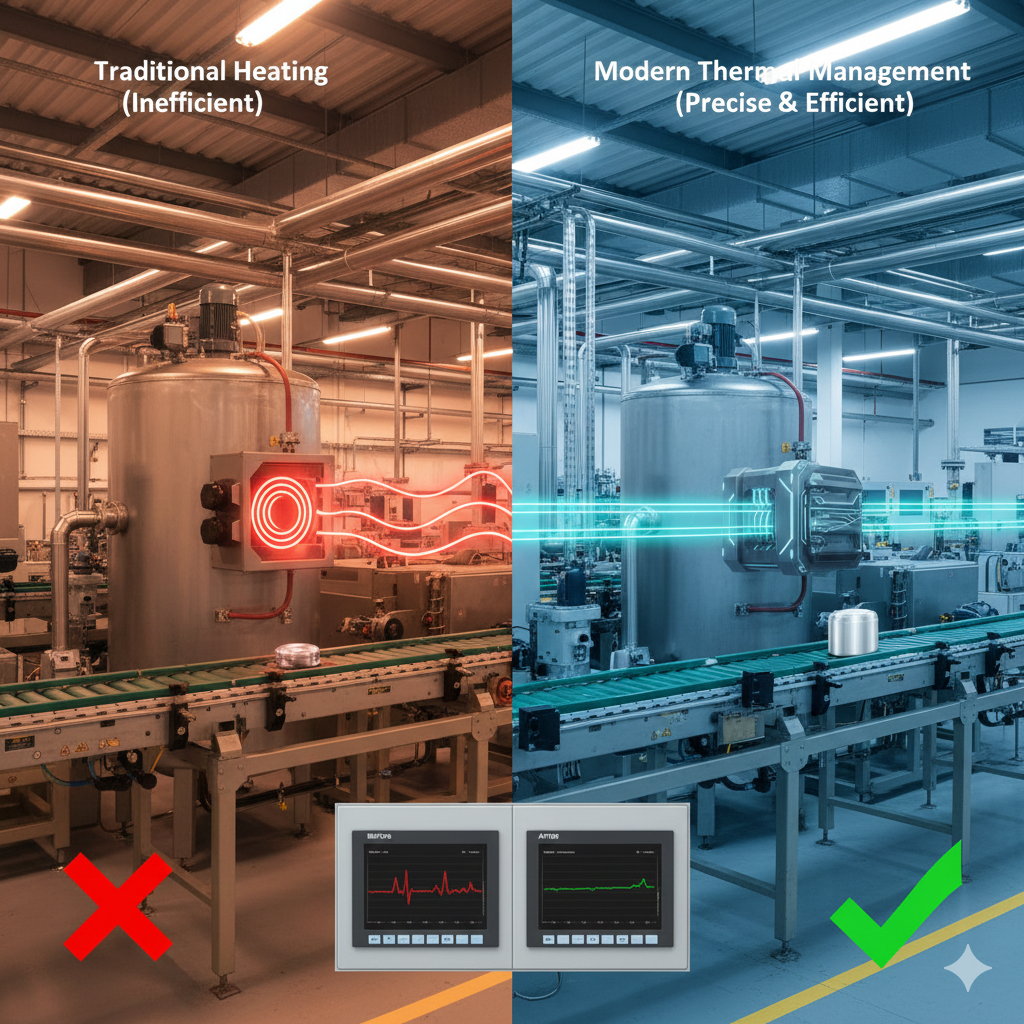
High Energy Consumption and Rising Costs
Traditional electric heaters operate with COP ≈ 1, resulting in significant energy waste during continuous operation.
Poor Temperature Stability
Slow response and overshoot lead to temperature fluctuations that negatively impact product consistency.
Localized Overheating Risks
Concentrated heating elements create hot spots that accelerate equipment wear and material degradation.
Limited Scalability and Integration
Traditional heaters are often bulky and difficult to integrate into compact or evolving industrial equipment.
High Maintenance and Downtime
Repeated thermal cycling shortens heater lifespan and increases unplanned maintenance events.
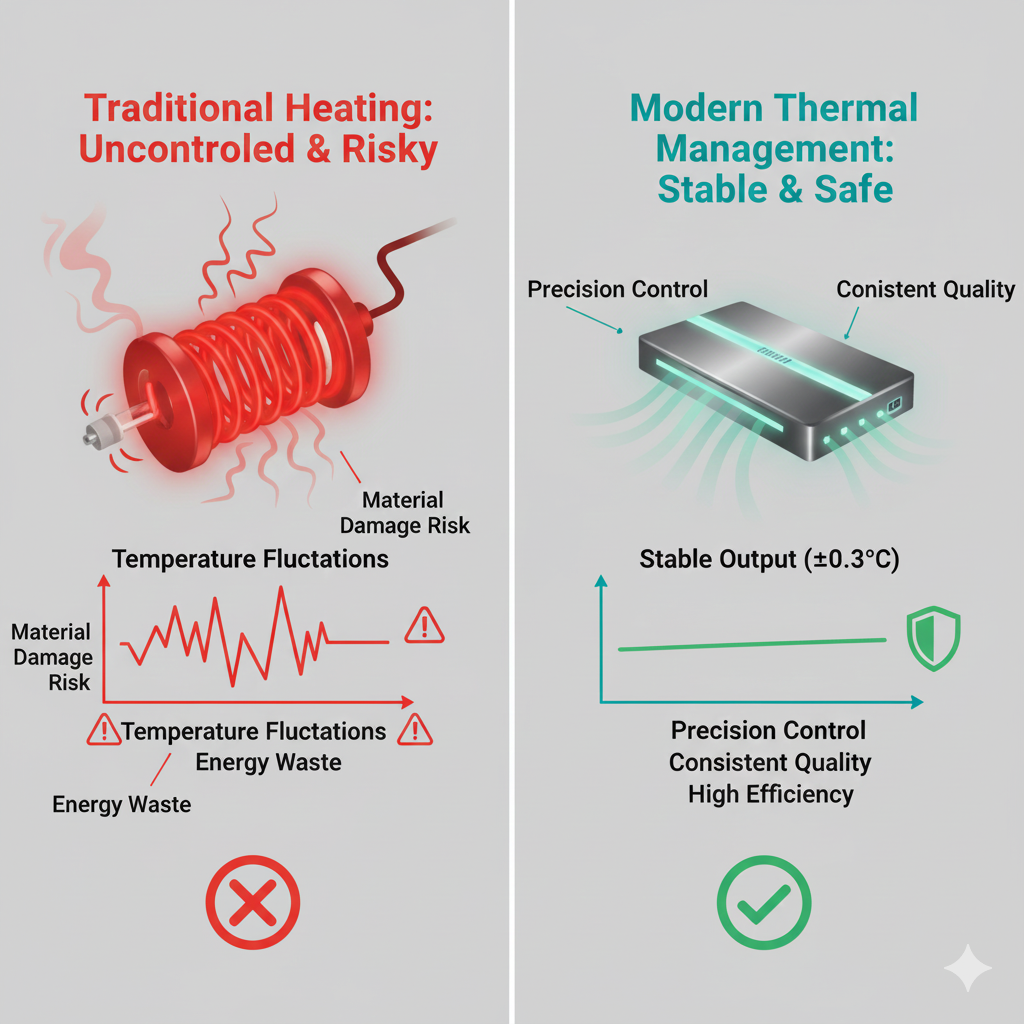
Working Principle (Step-by-Step)
Step 1: Efficient Thermal Energy Establishment
The system establishes a high-efficiency thermal source optimized for industrial operation.
Step 2: Thermal Energy Optimization
Heat is amplified or conditioned through advanced thermal transfer mechanisms.
Step 3: Controlled Heat Delivery
Thermal energy is evenly transferred to target equipment or process zones.
Step 4: Real-Time Monitoring
Sensors continuously collect temperature data across critical locations.
Step 5: Closed-Loop Control
Intelligent algorithms adjust output dynamically to maintain stable temperatures.
Step 6: Continuous Stable Operation
The system sustains long-term operation with minimal energy input and reduced electrical stress.
Case Study
Background
A manufacturing facility required stable process heating between 60°C and 85°C for high-precision industrial equipment.
Solution
Traditional electric heaters were replaced with an advanced electric heater alternative designed for seamless integration.
Results
- Energy consumption reduced by approximately 35–45%
- Temperature stability improved to ±0.3°C
- Maintenance frequency significantly reduced
- Overall equipment uptime increased
Comparison with Traditional Heating
| Dimension | Electric Heater Alternative | Traditional Electric Heater |
|---|---|---|
| energy efficiency | High (COP > 2) | Low (COP ≈ 1) |
| Temperature Stability | High precision | Fluctuations common |
| Heat Distribution | Uniform | Localized hot spots |
| Operating Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Maintenance | Low | Frequent |

FAQ
1. Is this suitable for continuous industrial operation?
Yes, it is designed for long-term operation.
2. Does replacement require major redesign?
No, integration is typically straightforward.
3. When are energy savings realized?
Often within the first year.
4. Is reliability higher than electric heaters?
Yes, due to reduced thermal stress.
5. How precise is temperature control?
High-precision closed-loop regulation.
6. Is initial investment higher?
Possibly, but lifecycle cost is lower.
7. Can it operate in harsh environments?
Yes, industrial-grade design.
8. Is customization supported?
Yes, temperature range and capacity are configurable.
Authoritative Conclusion
Replacing traditional electric heaters with advanced electric heater alternatives enables industrial equipment to achieve superior energy efficiency, temperature stability, and long-term reliability.
These solutions are rapidly becoming the new standard for modern industrial heating systems focused on performance, sustainability, and operational excellence.
 energy efficient industrial heating solution future" width="1024" height="1024" />
energy efficient industrial heating solution future" width="1024" height="1024" />