Pre-prepared food production is a complex process covering multiple links such as raw material processing, heating and cooking, sterilization, cooling, packaging and cleaning, with large energy consumption requirements and diverse links. High-temperature heat pumps recycle waste heat in production, raise low-grade heat energy to high temperature, and reuse it in cooking, sterilization and cleaning. This not only greatly reduces energy consumption, but also improves production efficiency and environmental friendliness.
Main heat-using links in pre-prepared food production
- Raw material cleaning and pretreatment
- Process: Clean, sterilize and precook raw materials such as meat and vegetables.
- Temperature requirements: Cleaning water temperature 60~90°C, sterilization temperature 80~100°C.
- Cooking and processing
- Process: High-temperature cooking of dishes, such as steaming, frying and stewing.
- Temperature requirements: Steaming temperature 100~120°C, frying temperature 150~200°C.
- Sterilization
- Process: After the finished product is packaged, high-temperature sterilization is carried out to ensure food safety.
- Temperature requirement: Sterilization temperature is 100~121°C.
- Cooling and packaging
- Process: The dishes are quickly cooled to 4~10°C before packaging.
- Source of waste heat: A large amount of low-temperature waste heat (30~50°C) is emitted during the cooling process.
- Equipment cleaning
- Process: Production equipment and pipelines need to be cleaned and sterilized at high temperature regularly.
- Temperature requirement: The cleaning water temperature is generally 60~90°C.
- Waste heat emission
- Source: Condensation heat and wastewater heat (50~70°C) generated during cooking, sterilization and cooling.
Application scenarios of high-temperature heat pumps
- Recovery of waste heat from cooking and sterilization
The cooking and sterilization process generates a large amount of condensation waste heat (temperature 60~80°C). High-temperature heat pumps can recover this waste heat and raise it to 100~120°C for the next batch of cooking or sterilization.
- Recovery of cooling waste heat
The low-temperature waste heat (30~50°C) released in the cooling process can be raised to 60~90°C by high-temperature heat pumps for equipment cleaning or preheating of cleaning water.
- Heat recovery from frying
The heat energy lost during frying can be recovered by high-temperature heat pumps and used in other heating processes, such as pre-cooking or sterilization.
- Heat recovery of cleaning wastewater
The heat of wastewater (temperature 40~60°C) discharged after equipment cleaning can be recovered by high-temperature heat pumps and used to heat a new round of cleaning water or other heat needs.
- Comprehensive management of thermal energy
High-temperature heat pumps can integrate low-grade thermal energy from various production links, and through centralized recovery and distribution, build an efficient thermal energy circulation system to meet the needs of cooking, sterilization, cleaning and other links.
Economic and environmental benefits
- Energy saving and consumption reduction
- High-temperature heat pumps recycle waste heat to replace boilers or electric heating, and the energy efficiency ratio (COP) can reach 3~5, which greatly reduces the use of external energy.
- Reduced operating costs
- Compared with traditional coal-fired or gas-fired boilers, the operating costs are significantly reduced. For example: the electricity cost of high-temperature heat pumps is much lower than the fuel cost.
- Reduce carbon emissions
- Reduce the use of fossil fuels and reduce the emission of carbon dioxide and other pollutants.
- Improve production efficiency
- High-temperature heat pumps provide stable and controllable heat to ensure the high and low temperature process requirements in the production of Pre-prepared dishes and improve product quality.
- Help sustainable development
- Comply with the concept of green manufacturing and enhance the environmental competitiveness of enterprises.
Case analysis
Background data:
- A pre-prepared food factory produces 100 tons per day.
- 2,000 kW of heat is required for cooking, and 1,500 kW of heat is required for sterilization.
- Total waste heat emission (temperature 60~80°C) is 2,000 kW.
Energy consumption calculation:

Savings:
The cost savings per hour is , 20 hours of operation per day, 300 days of operation per year, and the annual cost savings are:
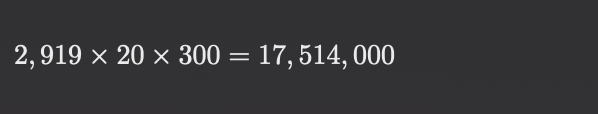
Carbon emission reduction:
The coal consumption is reduced by 3,743 kW. According to the coal carbon emission coefficient of 0.7 kg CO₂/kWh, the annual emission reduction is:

Conclusion
The application of high-temperature heat pumps in the production of pre-prepared dishes can provide the required heat energy for each process link by efficiently recovering the waste heat from the cooking, sterilization and cooling links, which not only significantly reduces energy costs, but also greatly reduces carbon emissions, helping enterprises achieve green production goals. At the same time, the application of high-temperature heat pumps ensures the stability and efficiency of heat supply, improves product quality and production efficiency, and provides an economical and efficient heat energy solution for the pre-prepared dish industry.


