As a Chinese herbal beverage, Wanglaoji herbal tea has a production process that includes raw material cleaning, decoction extraction, concentration, sterilization, filling and cleaning, which has a high demand for heat energy and generates a large amount of waste heat emissions. The application of high-temperature heat pumps can recycle waste heat in production, heat it up and reuse it in decoction, sterilization and cleaning, etc., to achieve energy conservation and carbon emission reduction.
Main heat-using links in Wanglaoji production
- Raw material cleaning
- Process: Herbal tea raw materials such as Chinese herbal medicines and auxiliary materials need to be cleaned.
- Temperature requirements: The cleaning water temperature is about 40~60°C.
- Decoction and extraction
- Process: Decoction of Chinese herbal medicines to extract effective ingredients.
- Temperature requirements: Decoction temperature 90~120°C.
- Concentration
- Process: Concentrate the decoction to increase the concentration of effective ingredients.
- Temperature requirements: Evaporation and concentration require heat temperature of 100~130°C.
- Sterilization
- Process: Sterilize the finished product at high temperature to ensure food safety.
- Temperature requirement: Sterilization temperature 121~135°C.
- Cooling and filling
- Process: After the product is cooled, it enters the filling stage.
- Source of waste heat: Heat discharged from cooling water (temperature 30~50°C).
- Equipment cleaning
- Process: Regular cleaning and disinfection of production equipment and pipelines.
- Temperature requirement: Cleaning water temperature is about 60~90°C.
- Waste heat discharge
- Source: Low-grade waste heat (50~80°C) will be generated in the boiling, sterilization, cooling and cleaning stages.
Application scenarios of high-temperature heat pumps
- Recovery of waste heat from boiling
The condensation heat (temperature 60~80°C) discharged from the boiling stage can be recovered by high-temperature heat pumps and raised to 90~120°C for the next batch of boiling or concentration processes.
- Utilization of sterilization waste heat
The high-temperature condensation waste heat generated in the sterilization process can be raised to 120~135°C by a High-temperature heat pump and then used for sterilization or other high-temperature demand processes.
- Recovery of cleaning waste heat
The heat energy of wastewater discharged in the cleaning process (40~60°C) can be recovered and heated to 60~90°C for preheating equipment cleaning water.
- Integration of heat energy cycle
The high-temperature heat pump recycles the waste heat in the production process to form an efficient heat energy cycle system to meet the heat energy requirements of multiple process links such as decoction, sterilization, and concentration.
Economic and environmental benefits
- Energy saving and consumption reduction
- High-temperature heat pumps replace traditional boilers, recycle waste heat, reduce the demand for new heat sources, and increase energy utilization by 30~50%.
- Reduced operating costs
- Compared with traditional coal-fired boilers or electric heating, the operating cost of high-temperature heat pumps is significantly reduced, and the energy consumption cost per ton of product is reduced by 20~40%.
- Reduce carbon emissions
- Reduce the use of fossil fuels, which can reduce thousands of tons of carbon dioxide emissions each year and help companies achieve their carbon neutrality goals.
- Improve production efficiency
- High-temperature heat pumps provide a stable heat source to ensure efficient operation of decoction, sterilization and other links, and improve product quality.
Case analysis
Background data:
- A certain Wanglaoji production line produces 500 tons of herbal tea per day.
- Decoction requires 3,000 kW of heat, and sterilization requires 2,500 kW of heat.
- Waste heat emissions are 3,500 kW (temperature 50~80°C).
Energy consumption calculation:
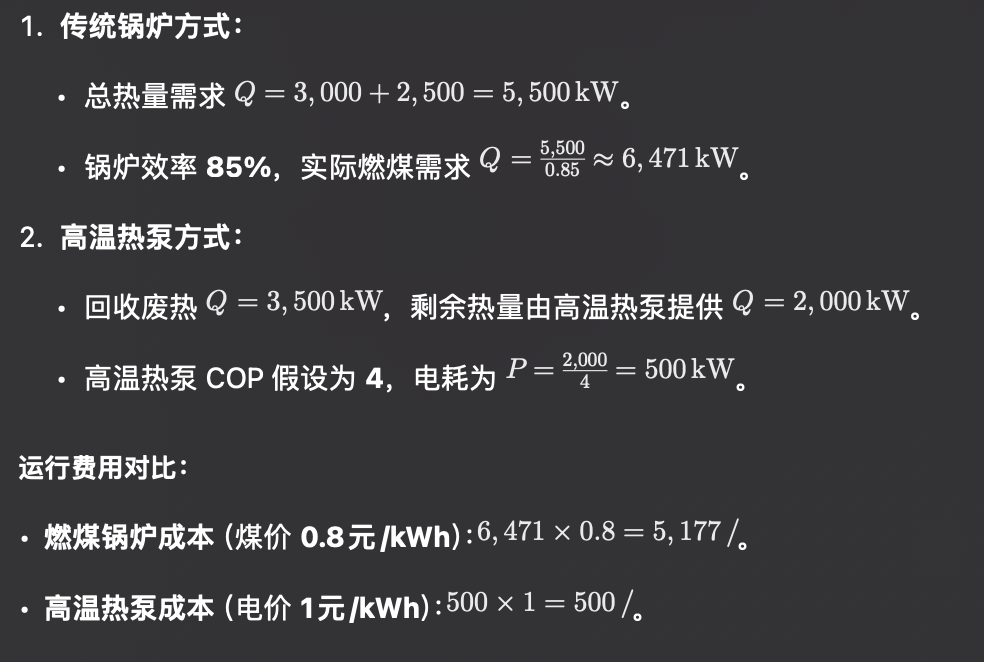
Savings:
The cost savings per hour is , 20 hours of operation per day, 300 days of operation per year, and the annual cost savings are:
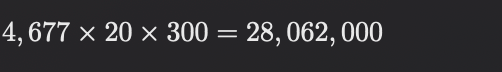
Carbon emission reduction:
Reduced coal consumption by 4,471 kW, calculated based on the coal carbon emission coefficient of 0.7 kg CO₂/kWh, the annual emission reduction is:

Conclusion
The application of high-temperature heat pumps in Wanglaoji production has greatly reduced the production heat demand and operating costs by efficiently recovering waste heat from decoction, sterilization, cooling and other links. At the same time, it reduces carbon emissions, achieves energy conservation and emission reduction, and provides an economical, efficient, environmentally friendly and low-carbon solution for herbal tea production. In the future, high-temperature heat pump technology will become a core driving force for the herbal tea production industry to enhance competitiveness and achieve green manufacturing.


