The bean paste production process includes raw material cooking, fermentation, sterilization, concentration, filling and other links, among which a large amount of heat energy demand is concentrated in the heating, cooking and sterilization stages. At the same time, waste heat (such as wastewater heat in the cooking, concentration and cleaning links) will be generated in the production process. If these low-grade heat energies are directly discharged, it will cause energy waste. High-temperature heat pump technology can effectively reduce production costs, reduce carbon emissions, and improve production efficiency by efficiently recovering waste heat and heating it for production processes.
Main heat-using processes for bean paste production
- Raw material cooking
- Process: Heat and cook beans or bean paste to soften them for subsequent fermentation.
- Temperature requirement: Usually 90~100°C.
- Fermentation temperature control
- Process: A suitable temperature needs to be maintained during the fermentation process to promote microbial activity.
- Temperature requirement: Generally controlled at 35~40°C.
- Sterilization
- Process: High temperature sterilization is performed before product packaging to ensure food safety.
- Temperature requirement: 100~120°C heat is required.
- Concentration
- Process: By heating the concentrated bean paste, the water content is reduced to meet the final product standards.
- Temperature requirement: Usually 80~110°C.
- Cleaning and disinfection
- Process: High temperature hot water is required for cleaning and disinfection of equipment and pipelines.
- Temperature requirement: The temperature of cleaning water is 60~90°C.
Application scenarios of high temperature heat pumps
- Recovery of waste heat from cooking
The cooking process will emit a large amount of steam condensation waste heat, with a temperature of about 60~80°C. High temperature heat pumps can recover this waste heat and raise its temperature to 90~100°C for re-cooking or concentration.
- Effect: Greatly reduce the steam consumption of boilers and improve energy efficiency.
- Utilization of waste heat from concentration
The condensation waste heat (about 50~70°C) generated during the concentration process can be heated to 80~110°C by a high-temperature heat pump for further concentration or sterilization.
- Case: Use a high-temperature heat pump to achieve a closed loop of heat energy in the concentration and sterilization stages.
- Heat recovery of cleaning wastewater
The heat of wastewater discharged from cleaning equipment and pipelines (temperature of about 40~60°C) can be recovered by a high-temperature heat pump and heated to 80~90°C for subsequent cleaning and disinfection processes.
- Effect: Reduce the demand for external hot water supply and improve the utilization rate of water resources.
- Comprehensive thermal energy management
Using a high-temperature heat pump to centrally recover and upgrade the low-grade heat energy generated during the production process can provide the required heat energy for multiple process links (such as sterilization, cleaning, and concentration), forming a complete thermal energy closed-loop system.
- Effect: Reduce energy waste and achieve overall energy-saving optimization of the production line.
Economic and environmental benefits
- Save energy costs
- Traditional methods rely on coal-fired boilers or electric heating, and high-temperature heat pumps use waste heat to provide heat energy, with an energy efficiency (COP) of 3~5, significantly reducing energy consumption.
- Reduce carbon emissions
- Reduce the use of fossil fuels, reduce greenhouse gas and other pollutant emissions, and help companies achieve carbon peak and carbon neutrality goals.
- Improve production efficiency
- The heat energy provided by high-temperature heat pumps is stable and controllable, which can meet the temperature control requirements of all links in the production of bean paste and improve product quality.
- Reduce maintenance costs
- Compared with traditional boilers, high-temperature heat pump systems have low operating and maintenance costs and long service life.
Case analysis
Background data:
- A bean paste factory produces 50 tons per day.
- The steaming stage requires 90°C heat and a heat load of 1,000 kW.
- The concentration stage requires 800 kW of heat, and 500 kW of waste heat (temperature 60°C) can be used.
- Use high-temperature heat pumps to replace part of the boiler for heating.
Energy consumption calculation:
- Traditional boiler method:
- Heat required for cooking .
- Heat required for concentration .
- Boiler efficiency is about 85%, actual fuel demand .
- High-temperature heat pump method:
- Recover waste heat 500 kW, high-temperature heat pump provides waste heat 1,300 kW.
- Heat pump COP is assumed to be 4, and power consumption is .
Operation cost comparison:
- Coal-fired boiler cost (based on coal price 0.8 yuan/kWh):
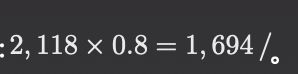
- High-temperature heat pump cost (based on electricity price 1 yuan/kWh):

Savings:
The cost savings per hour are , 16 hours of operation per day, 300 days of operation per year, and the annual cost savings are approximately:
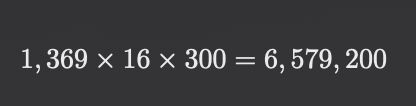
Carbon emission reduction:
The coal consumption is reduced by 1,793 kW. According to the coal carbon emission coefficient of 0.7 kg CO₂/kWh, the annual emission reduction is:

Conclusion
The application of high-temperature heat pumps in the production of bean paste can achieve efficient reuse of heat energy by recycling waste heat from cooking and concentration, reduce boiler fuel consumption, and reduce operating costs and carbon emissions. For food processing companies pursuing green production and energy saving and consumption reduction, high-temperature heat pumps are an ideal technical solution.


