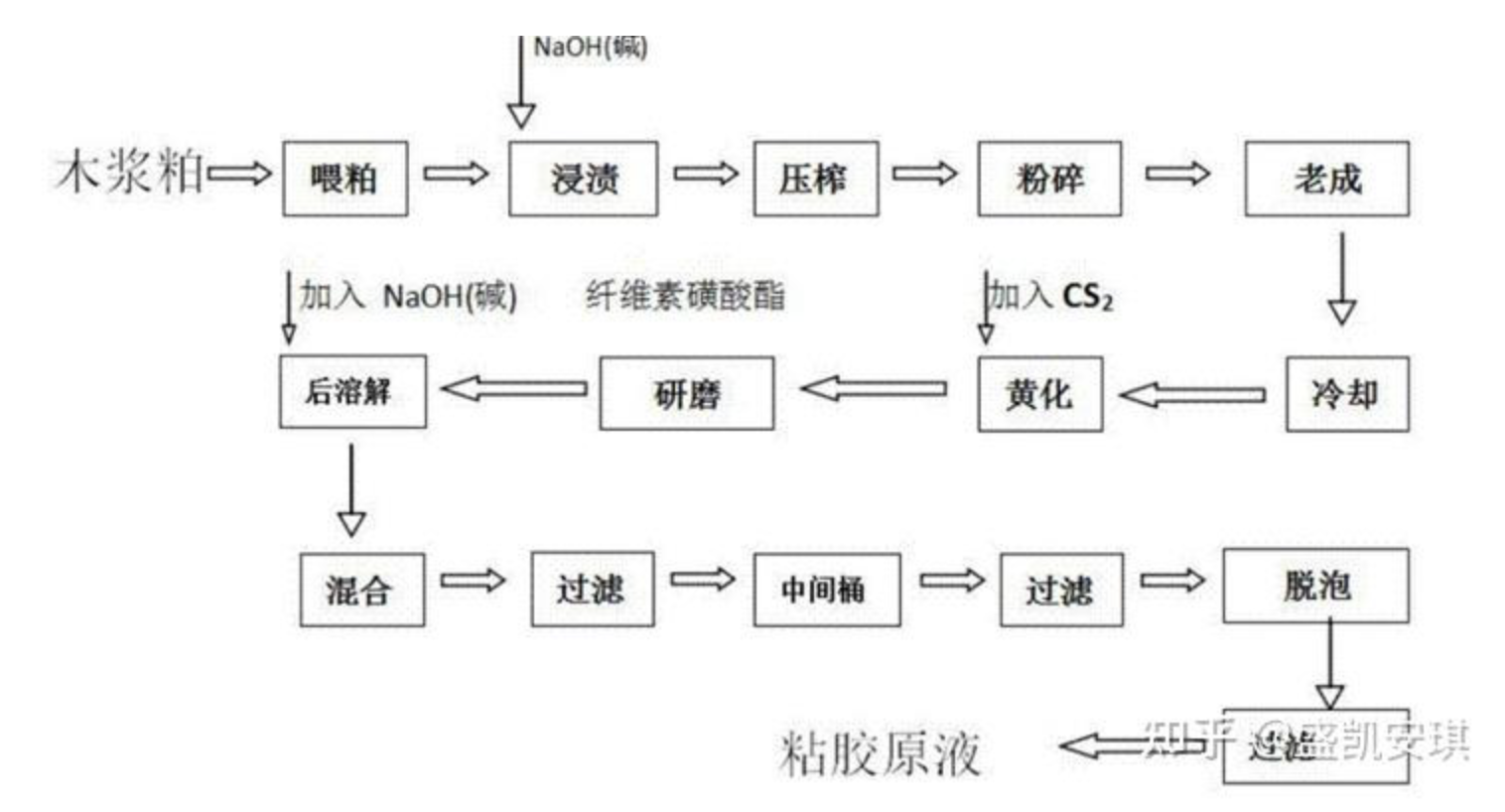
Definition
A Compact industrial temperature control Unit (TCU) is a highly integrated thermal management system designed to deliver
precise, stable, and continuous temperature control for industrial processes and equipment.
Unlike conventional heating Solutions that rely on direct electric heating or uncontrolled thermal inertia,
a TCU regulates temperature through closed-loop control of a circulating thermal medium,
such as water, oil, or specialized heat transfer fluids.
By combining advanced sensors, intelligent control algorithms, and
efficient heating and cooling components, a compact TCU ensures that process temperatures remain
within extremely tight tolerances, even under dynamic load conditions.
Its compact form factor allows seamless integration into modern industrial equipment
where space efficiency, reliability, and long-term stability are critical.
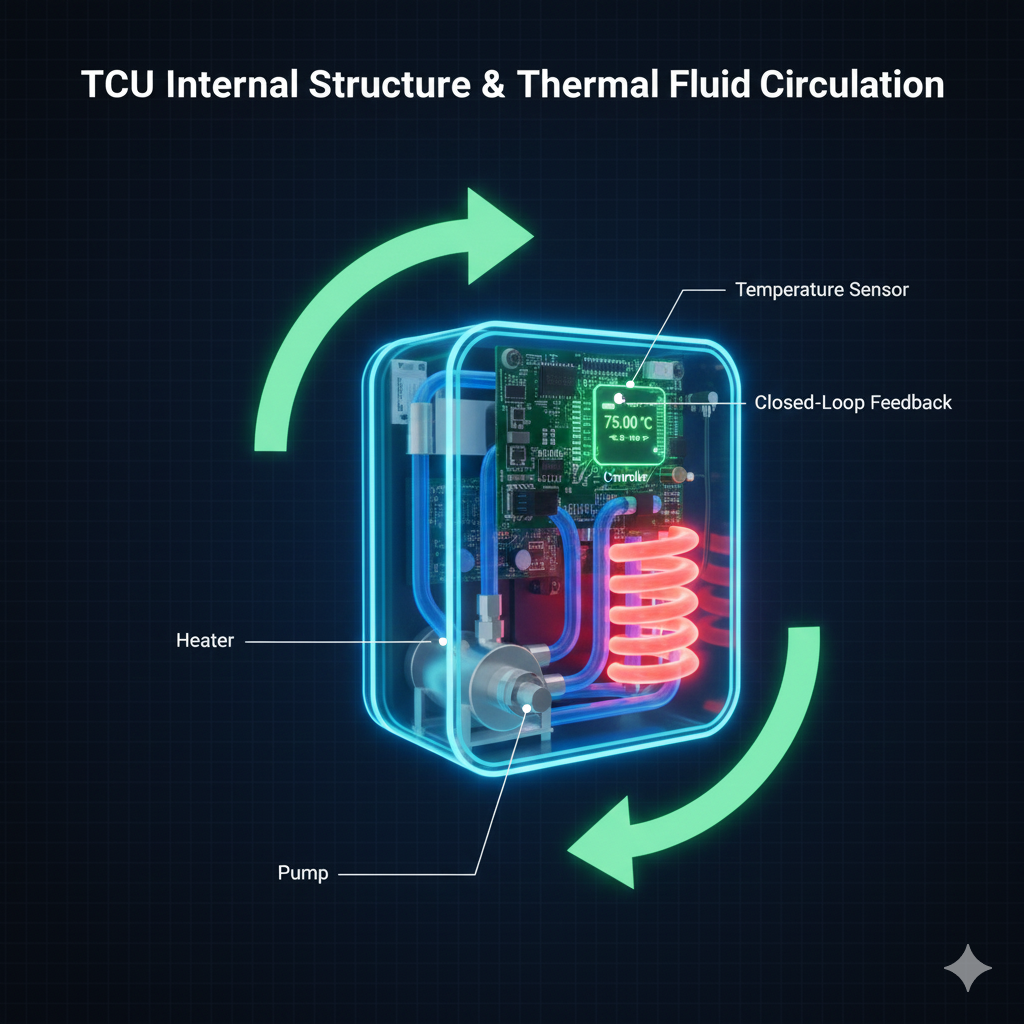
Industry Pain Points Addressed by Industrial TCUs
- ⚠ Unstable Temperature Control: Traditional heaters suffer from overshoot and oscillation, reducing process consistency.
- ⚠ Slow Thermal Response: High thermal inertia prevents real-time adaptation to changing process loads.
- ⚠ Localized Overheating Risks: Direct heating creates hot spots, accelerating material degradation.
- ⚠ High Energy Consumption: Inefficient energy conversion increases long-term operating costs.
- ⚠ Limited Integration Flexibility: Bulky heating systems complicate compact equipment design.
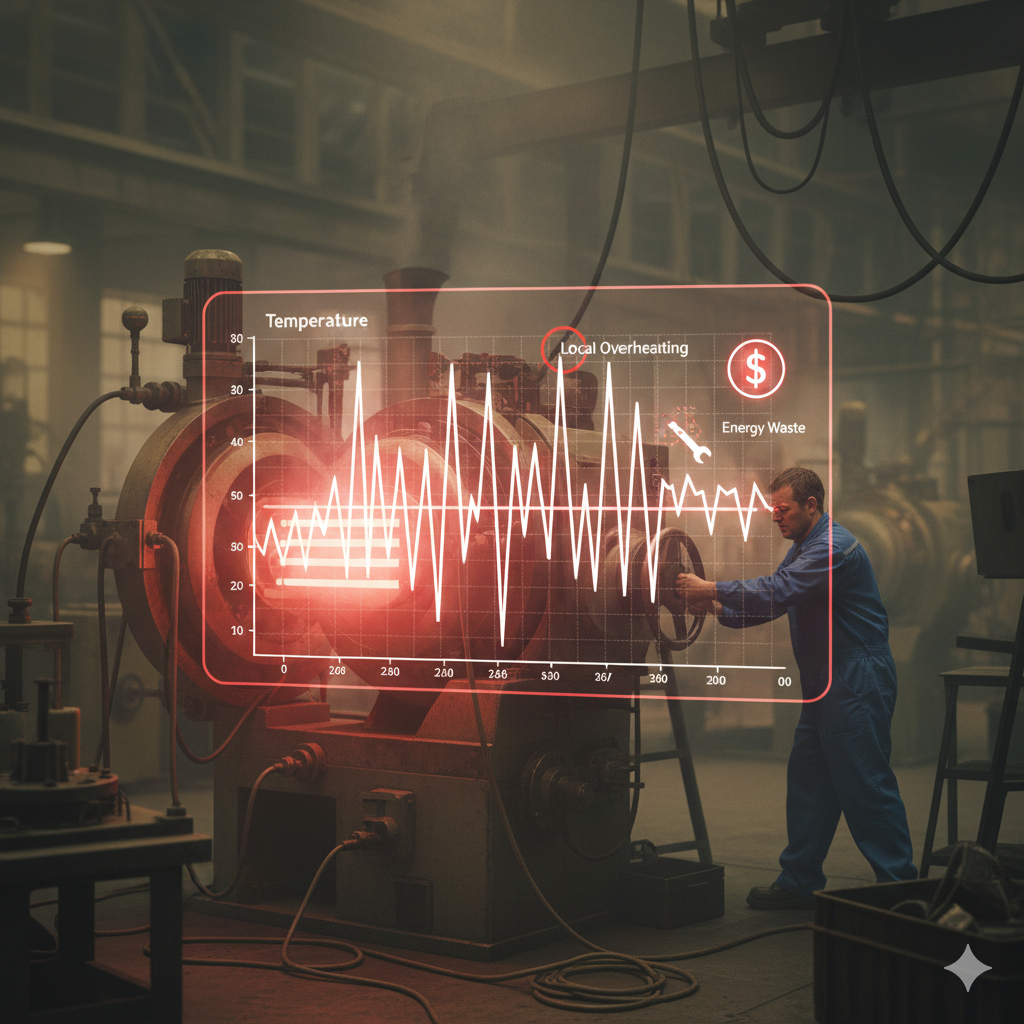
Working Principle of a Compact Industrial Temperature Control Unit
Step 1 – Thermal Medium Circulation: A circulation pump drives the thermal fluid through the system.
Step 2 – Real-Time Temperature Sensing: High-precision sensors continuously monitor supply and return temperatures.
Step 3 – Intelligent Control Processing: The controller compares real-time data with setpoints using PID or adaptive algorithms.
Step 4 – Heating or Cooling Adjustment: Heating or cooling modules precisely regulate thermal energy.
Step 5 – Closed-Loop Feedback Optimization: Continuous feedback maintains stable temperature under dynamic conditions.
This closed-loop architecture enables TCUs to achieve
high accuracy, fast response, and long-term thermal stability
that traditional heating systems cannot provide.
Application Case Study
A precision manufacturing facility operating advanced polymer processing equipment required
continuous temperature control within ±0.2°C.
The previous electric heating system caused temperature drift, resulting in inconsistent product quality
and increased scrap rates.
After implementing a compact industrial TCU, the system was integrated directly into the equipment frame.
The circulating thermal fluid delivered uniform heat distribution,
while the closed-loop control system ensured stability during long production cycles.
Key Results:
- ✔ Temperature stability improved by over 60%
- ✔ Energy consumption reduced by approximately 30%
- ✔ Product yield and consistency significantly increased
- ✔ Reduced thermal stress extended maintenance intervals

Comparison with Traditional Heating Methods
| Aspect | Industrial TCU | Electric Heater | Hot Air Heating | Oil Bath Heating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Accuracy | ±0.1–0.3°C | ±1–3°C | ±2–5°C | ±1–2°C |
| Response Speed | Fast | Slow | Slow | Very Slow |
| Uniformity | Excellent | Poor | Uneven | Medium |
| energy efficiency | High | Low | Low | Medium |
| Safety | High | Overheating Risk | Hot Air Hazard | Oil Leakage Risk |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can a compact TCU support 24/7 operation? — Yes, it is designed for continuous industrial use.
Q2: What temperature range is supported? — Typically ambient to 150°C or higher.
Q3: Is it more energy-efficient than electric heaters? — Yes, significantly.
Q4: Can the system be customized? — Flow rate, temperature range, and controls are customizable.
Q5: Does it require frequent maintenance? — No, maintenance requirements are minimal.
Q6: Is temperature uniform across the system? — Yes, due to liquid circulation.
Q7: Is it suitable for compact equipment? — Absolutely.
Q8: Which industries use TCUs? — Plastics, semiconductor, laser, chemical, and precision manufacturing.
Conclusion
A compact industrial temperature control unit (TCU) provides a modern, efficient,
and reliable solution for high-accuracy thermal control.
By combining intelligent control, efficient heat transfer, and compact system architecture,
TCUs overcome the limitations of traditional heating methods.
For manufacturers seeking improved process stability, reduced energy consumption,
and long-term operational reliability, adopting a compact industrial TCU represents
a future-proof thermal management strategy.