 low power industrial heating solution definition" width="1024" height="1024" />
low power industrial heating solution definition" width="1024" height="1024" />
Definition
A low power industrial heating solution refers to a thermal system designed to deliver stable, controllable, and continuous heat output while minimizing electrical power consumption.
Unlike traditional electric resistance heaters that convert electricity directly into heat, low power industrial heating Solutions rely on high-efficiency heat transfer mechanisms, intelligent control strategies, and optimized system integration to reduce energy input without sacrificing process stability.
In industrial environments where equipment operates continuously and temperature consistency directly affects product quality, this type of heating solution functions as a process optimization technology rather than a simple energy-saving device.

Key Industry Pain Points Addressed
High Energy Consumption and Rising Operating Costs
Traditional industrial heating systems consume power at a one-to-one ratio between electricity input and heat output. In continuous-duty applications, this leads to significant energy waste and escalating operational costs.
Temperature Instability and Process Inconsistency
Conventional heating methods often suffer from temperature overshoot, slow response times, and uneven heat distribution, resulting in product inconsistency and increased defect rates.
Electrical Infrastructure Constraints
High-power heaters increase peak load demand, frequently requiring costly upgrades to transformers, cabling, and power distribution systems.
Accelerated Equipment Wear
Frequent on/off cycling and localized overheating accelerate component aging, leading to shortened service life and higher maintenance frequency.
Sustainability and Compliance Pressure
Energy-intensive heating systems increasingly conflict with corporate sustainability goals and regulatory requirements.
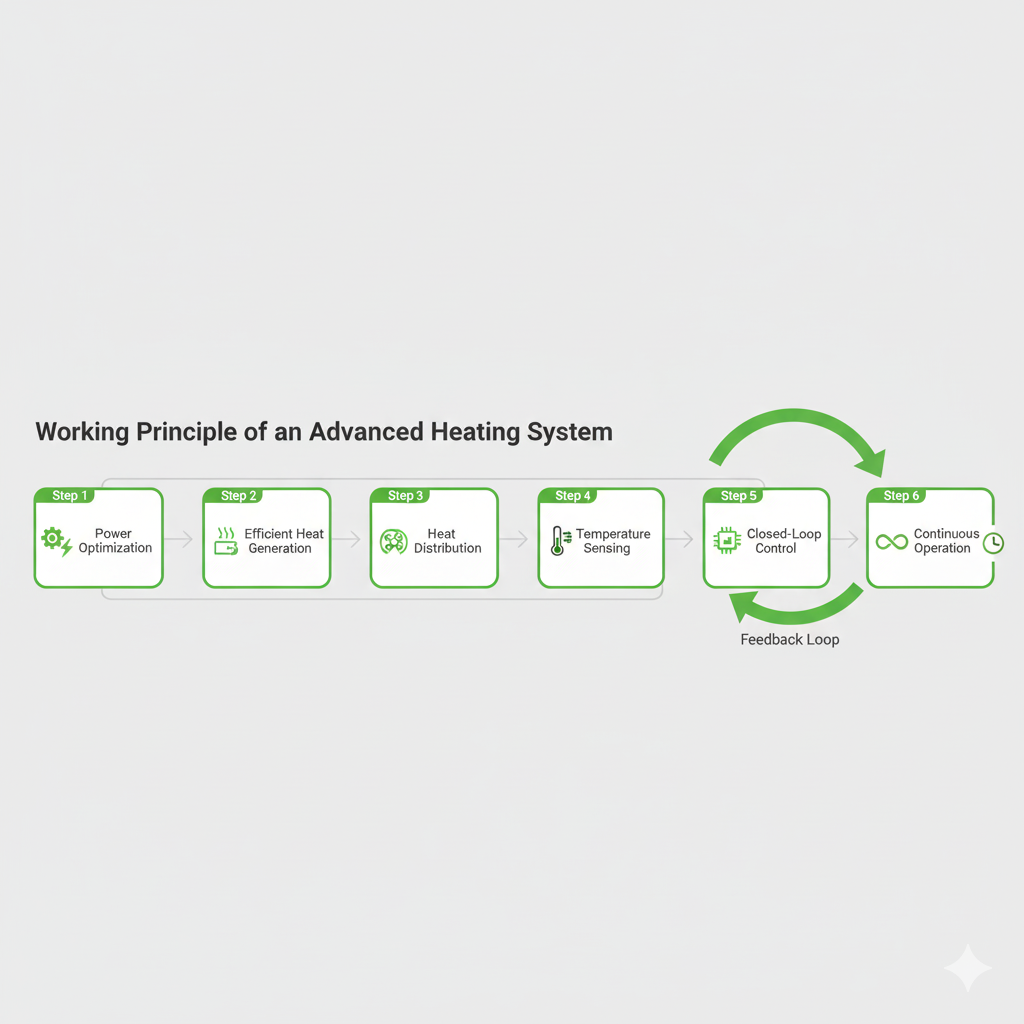
Working Principle (Step Structure)
Step 1 – Optimized Energy Input Management: Intelligent power modules regulate input and reduce peak electrical load.
Step 2 – Efficient Heat Generation or Transfer: Advanced thermal mechanisms improve heat utilization beyond resistive heating.
Step 3 – Precision Heat Distribution: Engineered thermal pathways ensure uniform temperature across process zones.
Step 4 – Real-Time Temperature Monitoring: High-accuracy sensors continuously track system conditions.
Step 5 – Intelligent Closed-Loop Control: Output is dynamically adjusted to match real-time thermal demand.
Step 6 – Continuous Low-Stress Operation: Steady-state operation minimizes wear and improves long-term reliability.
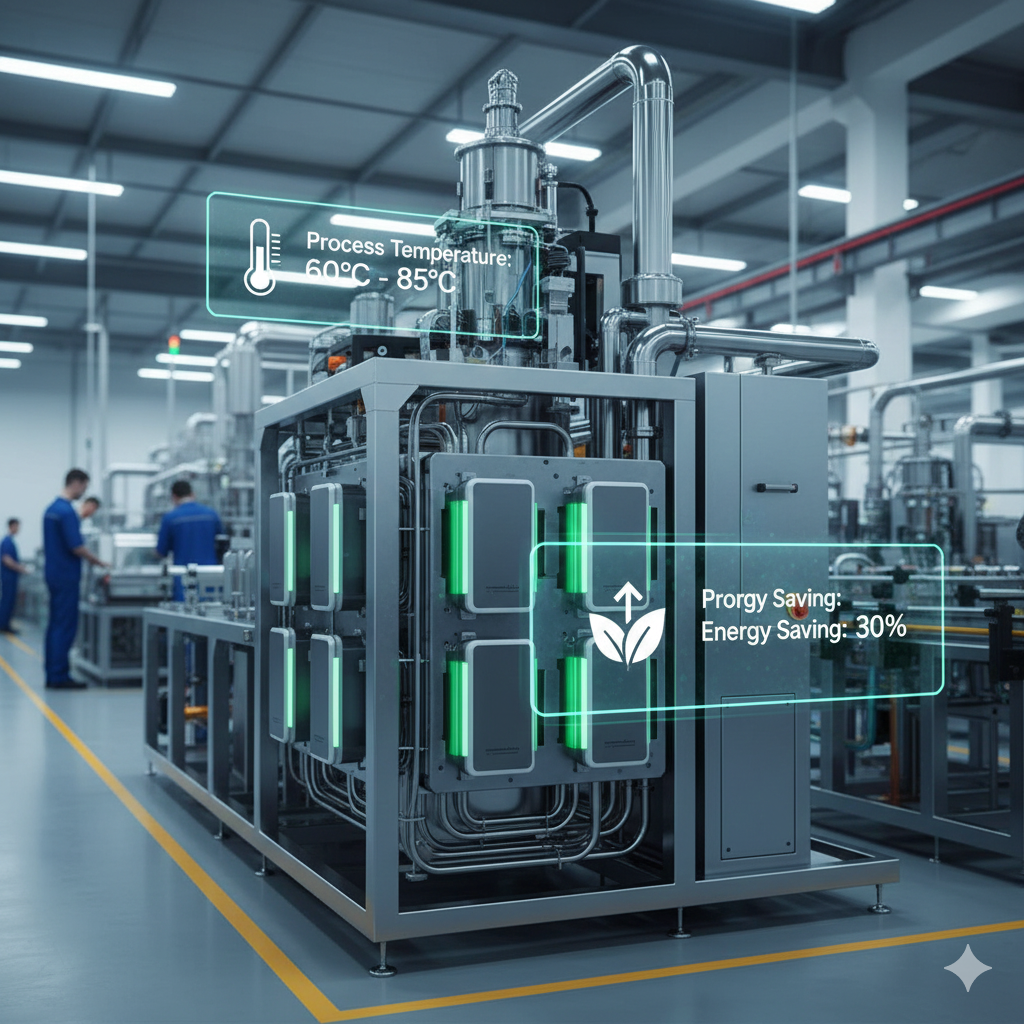
Industrial Application Case Study
A precision manufacturing facility operating 24/7 required stable heating between 60–85°C. Its existing electric resistance heaters caused high power consumption, temperature fluctuation, and frequent downtime.
After integrating a low power industrial heating solution, the facility achieved:
- 35–45% reduction in electrical power consumption
- Temperature stability improved to ±0.3°C
- Extended maintenance intervals
- Improved product consistency and yield

Comparison with Traditional Heating Methods
| Factor | Low Power Heating | Electric Heater | Hot Air | Oil Bath |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| energy efficiency | High | Low | Low | Low |
| Temperature Stability | Excellent | Moderate | Poor | Slow |
| Power Demand | Low & Stable | High | Medium | High |
| Maintenance | Low | High | Medium | High |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What defines a low power industrial heating solution?
A system delivering required heat with minimal electrical input.
Q2: Can it support continuous operation?
Yes, it is optimized for long-duration industrial processes.
Q3: Is temperature accuracy sufficient?
Yes, closed-loop control enables high precision.
Q4: Are infrastructure upgrades required?
Usually not, due to reduced power demand.
Q5: How is maintenance impacted?
Maintenance frequency is significantly reduced.
Q6: Is it safe?
Yes, lower thermal stress improves safety.
Q7: Which industries benefit most?
Manufacturing, electronics, battery, laboratory sectors.
Q8: Is ROI attractive?
Yes, long-term savings outweigh initial investment.

Authoritative Conclusion
A low power industrial heating solution represents a strategic advancement in industrial thermal management. By reducing energy consumption, stabilizing process temperatures, and minimizing operational stress, it directly addresses the most critical challenges faced by modern industrial facilities.
As industries move toward smarter, more sustainable production models, adopting low power industrial heating is not merely an upgrade—it is a fundamental step toward future-ready industrial processes.