battery thermal management heating system for industrial batteries" width="1024" height="1024" />
battery thermal management heating system for industrial batteries" width="1024" height="1024" />
Energy-efficient battery thermal management heating technology
refers to an integrated heating and control solution designed to actively regulate battery temperature
within an optimal operating range, particularly under low-temperature or variable environmental conditions.
Unlike passive insulation or conventional resistive heating, this technology focuses on
precise, intelligent, and energy-conscious thermal regulation
to ensure industrial battery systems operate safely, reliably, and efficiently throughout their lifecycle.
In industrial battery systems—such as energy storage systems (ESS), backup power units, off-grid installations,
and heavy-duty electric equipment—temperature stability directly impacts performance, safety, efficiency,
and longevity.

Key Industry Pain Points Addressed
- Severe performance degradation at low temperatures:
Reduced capacity, unstable voltage, and lower power output under cold conditions. - Cold start failures and system downtime:
Batteries may fail to initialize properly, compromising industrial reliability. - Accelerated aging and safety risks:
Low-temperature operation increases internal resistance and degradation risks. - High energy consumption from traditional heating:
Resistive heaters consume excessive energy with poor control. - Limited system integration:
Conventional Solutions lack intelligent coordination with BMS or controllers.
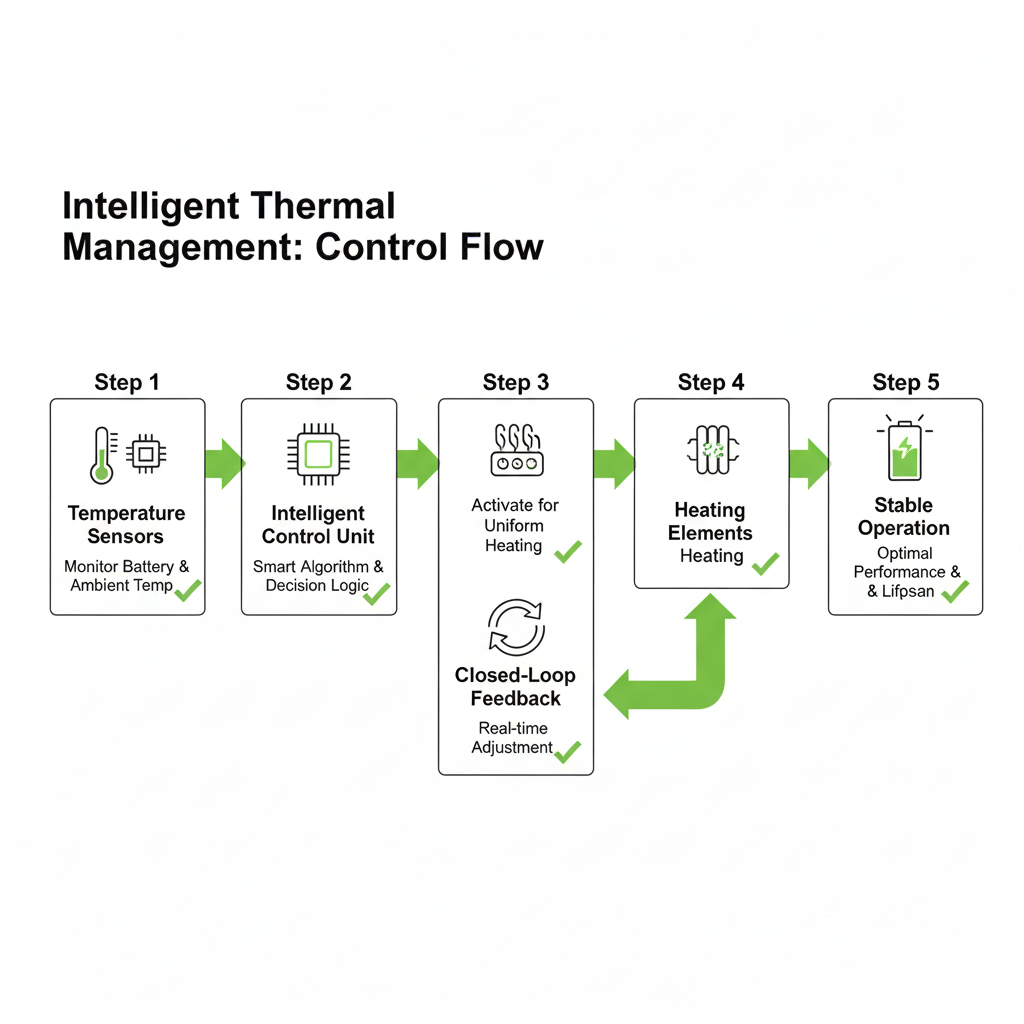
Working Principle (Step-by-Step)
Step 1 – Real-Time Temperature Monitoring
High-accuracy sensors continuously monitor battery cell and ambient temperatures.
Step 2 – Intelligent Control Logic
The control unit evaluates data against predefined thresholds and calculates heating demand.
Step 3 – Targeted and Uniform Heating
Heat is delivered directly and evenly to battery modules, avoiding thermal hotspots.
Step 4 – Closed-Loop Feedback Regulation
Continuous feedback dynamically adjusts heating power to maintain optimal temperature.
Step 5 – Standby and Maintenance Heating
Once optimal temperature is reached, low-power compensation maintains stability efficiently.
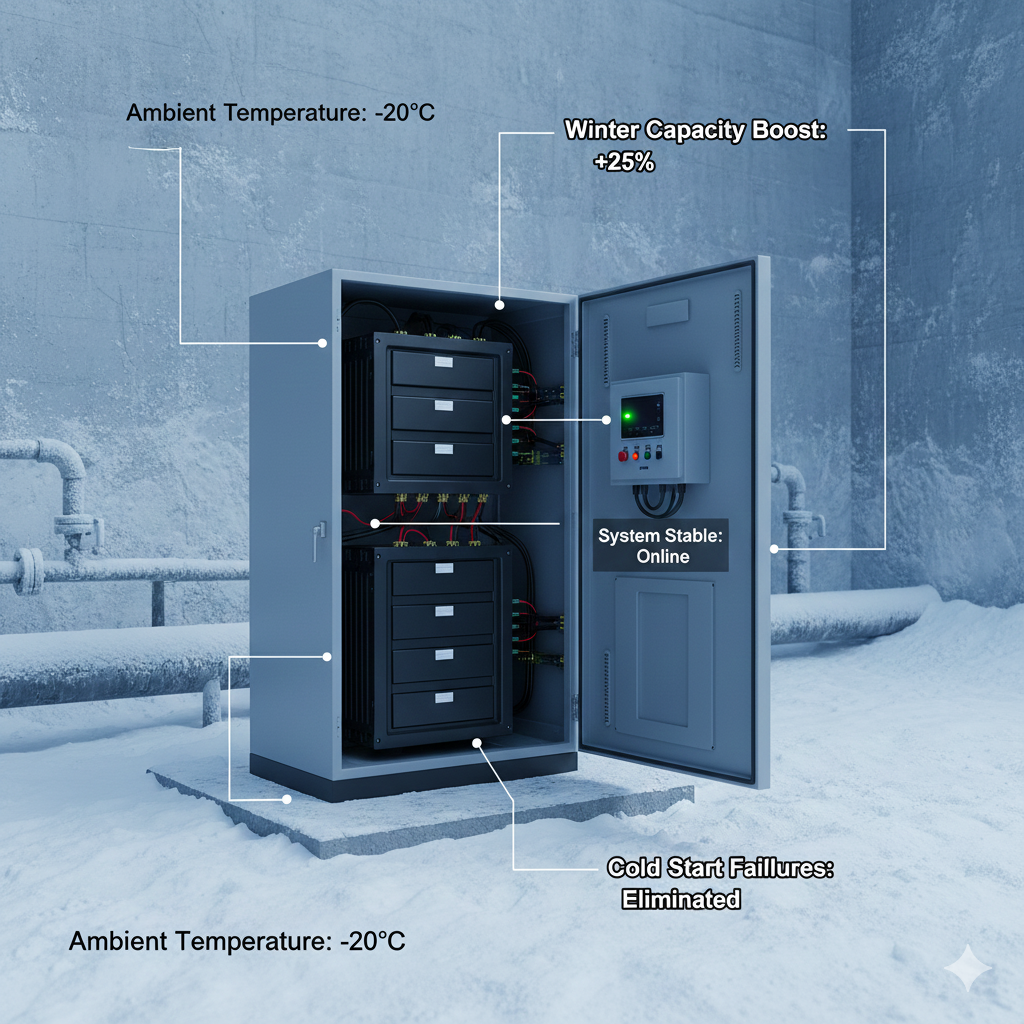
Case Study: Industrial Energy Storage System in Cold Climate
An industrial energy storage facility located in a northern region experienced recurring operational issues
during winter months, with ambient temperatures dropping below -20°C.
After integrating an energy-efficient battery thermal management heating system directly with the BMS,
batteries were preheated and maintained within an optimal operating range.
- Winter usable capacity increased by approximately 20–30%
- Cold start failures were virtually eliminated
- Heating energy consumption reduced by over 30%
- Battery lifespan significantly extended

Comparison with Traditional Heating Methods
| Dimension | Battery Thermal Management Heating | Resistive Heating | Ambient Heating |
|---|---|---|---|
| energy efficiency | High, targeted control | Low | Very low |
| Temperature Accuracy | Precise, closed-loop | Limited | Poor |
| Heating Uniformity | Excellent | Uneven | Uncontrolled |
| Safety | High | Overheating risk | Unpredictable |
| System Integration | Seamless with BMS | Limited | None |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Is thermal management heating necessary for all industrial battery systems?
- Does it significantly increase energy consumption?
- Can it be integrated with existing systems?
- Which battery chemistries are supported?
- How does it improve battery lifespan?
- Is long-term continuous operation safe?
- What maintenance is required?
- Can it operate in extremely low temperatures?

Authoritative Conclusion
Energy-efficient battery thermal management heating technology is a critical foundation for modern
industrial battery systems. By addressing low-temperature performance degradation, safety risks,
and excessive energy consumption, it enables stable, reliable, and long-term battery operation.
For industrial applications where reliability and efficiency are essential, this technology is
not optional—it is a system-level requirement.