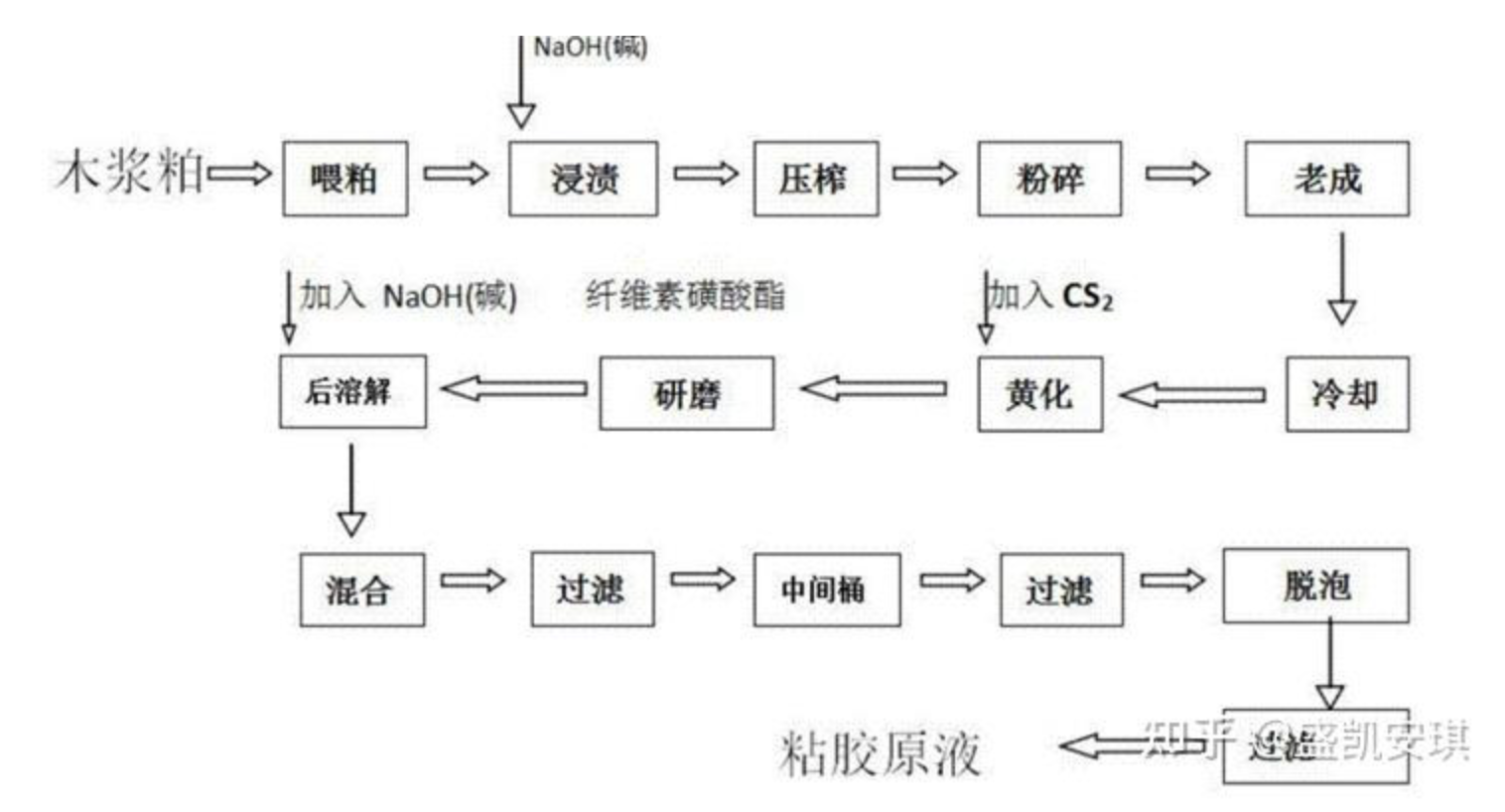
high-temperature heat pump has emerged as a leading solution for replacing conventional fossil-fuel heating systems.
Unlike standard heat pumps limited to 55–70°C output, industrial high-temperature heat pumps can deliver 80–120°C (and above in some designs) process heat,
enabling direct application in food processing, chemical production, drying, pharmaceuticals, textiles, and more.
This article explains how high-temperature heat pumps work, why they matter, and how they outperform gas and coal heating systems.
What Is a High-Temperature Heat Pump?
A high-temperature heat pump (HTHP) is an advanced heating system that extracts low-grade heat from sources such as ambient air, process exhaust, or water and upgrades it to high-temperature process heat through a vapor-compression or transcritical cycle.
Typical output range: 80°C hot water up to 95–120°C process heat (varies by refrigerant and system design).
- Uses refrigerants like CO₂ (R744), R1234ze, R245fa, etc.
- Delivers stable industrial-grade heat
- High efficiency and reduced fuel dependency
How High-Temperature Heat Pumps Work
The basic process is:
- Absorb low-temperature heat from air, water, or waste heat streams;
- Compress the refrigerant to raise its temperature and pressure;
- Release high-temperature heat into water/steam circuits or direct hot air systems;
- Expand and recycle the refrigerant in a closed loop with minimal loss.
This approach allows factories to convert electrical input into multiple units of useful heat (high COP), significantly lowering operational energy use compared with direct combustion.
Key Advantages Compared with Traditional Boilers
1. Much Lower Energy Cost
High-temperature heat pumps commonly achieve a COP of 2.5–4.0, which means 1 kWh of electricity can deliver 2.5–4 kWh of heat.
By comparison, modern gas boilers typically operate at 80–92% efficiency and coal boilers often below 70%.
2. Near-Zero On-Site Emissions
Boilers burn fuel and emit CO₂, NOx, SO₂, and particulates. Heat pumps produce heat without combustion, removing on-site emissions and helping factories meet stricter environmental standards.
3. Lower Maintenance and Higher Reliability
Heat pumps have no burners, chimneys, or fuel handling systems—resulting in lower maintenance frequency, simpler servicing, and less downtime.
4. Compatible with Renewable Power
Pairing heat pumps with rooftop solar, on-site wind, or low-carbon grid electricity further reduces lifecycle emissions and operating cost—an ideal path for manufacturers targeting net-zero.
Industrial Application Scenarios
Common industries and uses include:
- Food & beverage: pasteurization, cleaning, cooking, drying (80–95°C)
- Chemical processing: reaction heating, hot-water circulation (90–110°C)
- Pharmaceuticals: sterilization, hot-water systems (80–95°C)
- Textile dyeing: heat setting and dye baths (85–120°C)
- Rubber & plastics: vulcanization and process heating
Real Industrial Case Study — Food Processing Plant
Background
A medium-sized food factory used a 1-ton gas boiler to provide 90°C heat for mixing and sterilization. They faced rising fuel costs, unstable temperature control, and pressure from new carbon regulations.
Solution
The plant installed a purpose-built 90°C CO₂ high-temperature heat pump system that uses ambient and recovered process heat as inputs.
Results (Annualized)
| Performance Item | Gas Boiler | HTHP (CO₂) |
|---|---|---|
| energy efficiency | ~88% | COP 3.2 |
| Monthly Energy Cost | 100% baseline | -62% |
| CO₂ Emissions | High | Near zero (onsite) |
| Payback Period | N/A | ~1.8 years |
This real-world retrofit demonstrates clear energy and carbon benefits—especially in processes that require steady mid-range temperatures.
How This Helps Your Business & Brand
Adopting high-temperature heat pumps helps manufacturers reduce operating costs, lower emissions, and comply with tightening environmental rules. These benefits not only improve the bottom line but also strengthen brand reputation with customers and regulators.
To explore tailored Solutions, view our product and solution pages:
Zhenmingzhu Official Website.
SEO & Content Recommendations (Quick)
- Use the focus keyword “High-temperature heat pump” in the first 100 words and in one H2.
- Include 1–2 internal links to product/solution pages per article.
- Add one original image with
alt="High-temperature heat pump"for better indexing. - Publish 1–2 technical articles per week during the initial 2 months to build topical authority.
FAQ
Q: Can high-temperature heat pumps replace boilers?
A: For many processes up to ~135°C, yes—heat pumps can fully replace gas or coal boilers. Some extremely high-temperature steam applications may need hybrid systems.
Q: Is CO₂ safe as a refrigerant?
A: Yes. CO₂ (R744) is non-flammable, non-toxic, and has a GWP of 1, making it an environmentally preferred refrigerant for industrial systems.
Q: How quickly can I expect ROI?
A: Typical payback is 1.5–4 years depending on local energy prices, waste-heat availability, and project scale.