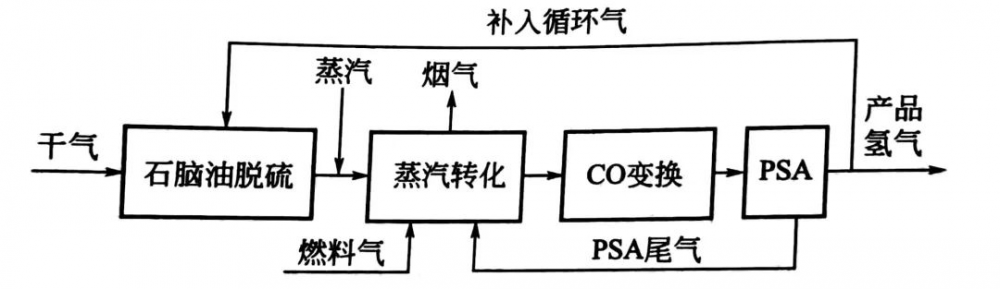
Chemical Fiber is a kind of fiber with textile properties made from natural polymer compounds through preparation, spinning, and post-processing.
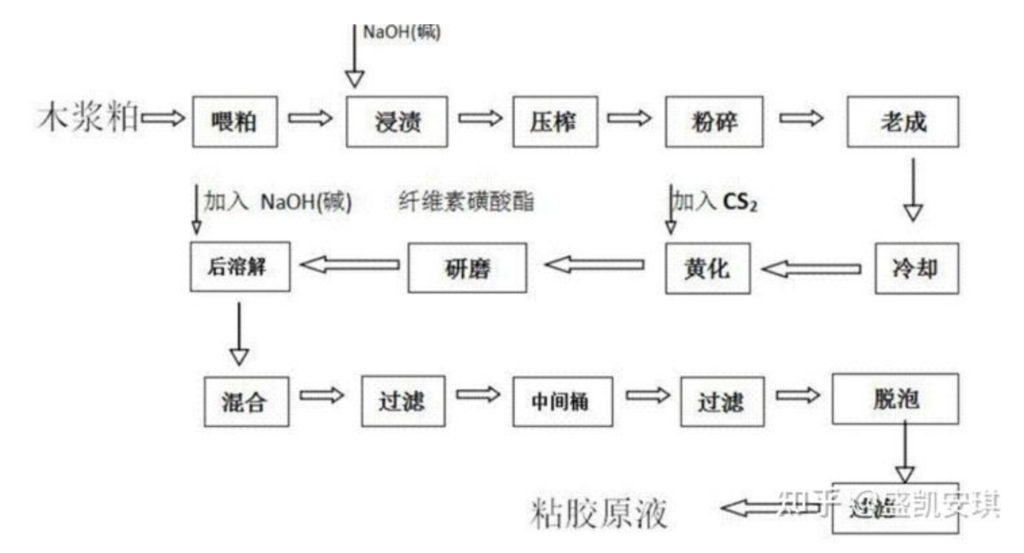
The preparation process of chemical fibers usually involves several key thermal processes and temperature controls, including the following aspects:
Polymerization reaction:
Polymerization temperature: In polymerization reactions, the reaction temperature is usually between 150°C and 300°C. Too low a temperature will lead to a decrease in the reaction rate, while too high a temperature may cause polymer degradation.
Dissolution process:
Dissolution temperature: When dissolving a polymer in a solvent, it is usually necessary to heat it to 60°C to 200°C, depending on the type of polymer and the nature of the solvent.
Spinning process:
Spinning temperature: During the spinning process, the temperature of the melt or solution is usually controlled between 200°C and 300°C. Temperature control directly affects the physical properties and processing performance of the fiber.
Drying and curing:
Drying temperature: Chemical fibers are generally dried at between 100°C and 150°C to remove residual solvents and moisture.
Heat treatment:
Heat setting: For some types of fibers, heat setting is performed at 150°C to 250°C to improve the crystallinity and stability of the fiber.
Cooling:
In the whole process, the cooling stage is also very important. The cooling temperature is usually controlled below room temperature to ensure the stability and strength of the fiber.
The above thermal process and temperature control are key factors to ensure the quality of chemical fibers, and different fiber materials and process requirements may vary.